As 2025 approaches, businesses must prepare for a wave of USA employee law changes that will significantly impact HR practices across the United States. From shifts in labor laws to new compliance mandates, these employee law changes aim to improve workplace standards while introducing new challenges for HR departments. Understanding these updates is essential for ensuring compliance, avoiding penalties, and fostering a positive employee experience.
As businesses prepare for the upcoming employee law changes in 2025, it’s essential to recognize how these updates align with the broader history of workplace regulations. Significant employee law changes have continually reshaped employment practices, setting the foundation for today’s evolving legal landscape.
Key USA Employee Law Changes for 2025
Federal Minimum Wage Increase
As of 2024, the federal minimum wage in the United States is $7.25 per hour. However, 30 states and the District of Columbia have established higher minimum wage rates. The remaining 22 states adhere to the federal minimum wage of $7.25 per hour. While the federal mandate establishes a baseline, states like California and Washington have already set higher minimum wages.
- California: Minimum wage in 2024 is 16.00$/hour, check how it’s going to change in 2025 for this state.
- Washington: Minimum wage is 16.28$/hour and will probably increase by 1.85% in 2025.
The states currently maintaining the federal minimum wage of $7.25 per hour are:
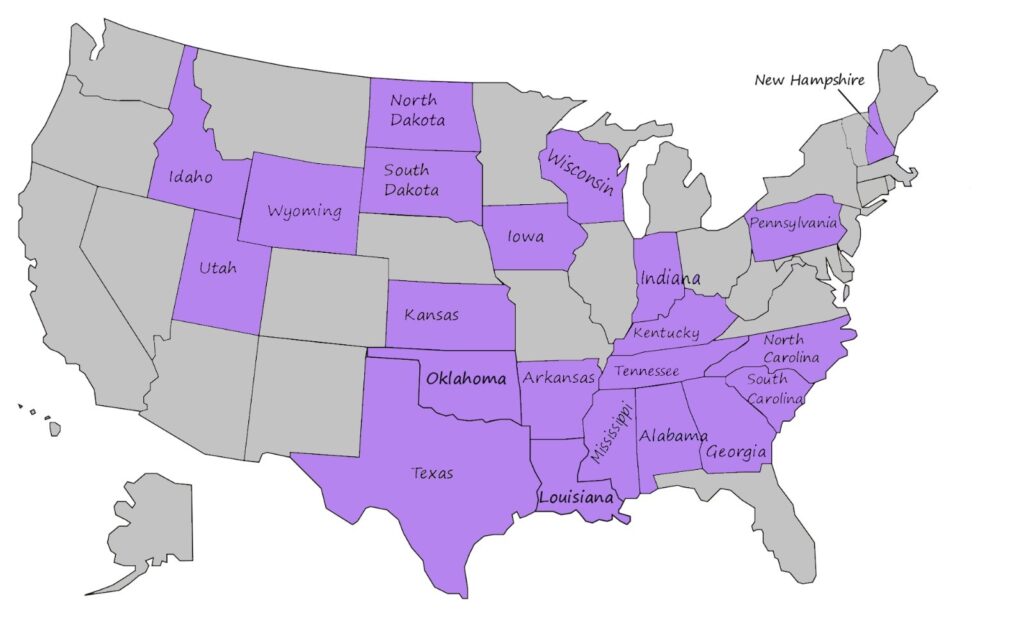
In these states, employers will need to adjust their payroll systems to comply with the new federal minimum wage of $10.50 per hour, effective January 1, 2025. This adjustment is crucial to ensure compliance with federal law and to provide fair compensation to employees.
It’s important to note that some states have not adopted a state minimum wage, defaulting to the federal rate. Additionally, certain states have minimum wages below the federal rate; in such cases, the federal minimum wage prevails.
Employers in the affected states should proactively update their payroll systems and budgets to accommodate the upcoming wage increase, ensuring compliance and supporting their workforce effectively.
For detailed information on the federal minimum wage increase, visit the U.S. Department of Labor’s official page.
New Overtime Requlations
The Department of Labor (DOL) is updating the overtime salary threshold to $58,0656 per year, up from the current $35,568. Employees earning less than this amount will now qualify for overtime pay. This Employee Law Change ensures fair compensation for millions of American workers.
Learn more about the new overtime rule in the DOL news release.
Impact on HR:
- HR teams must review employee classifications to ensure compliance.
- Potentially higher overtime costs may necessitate hiring additional staff or redistributing workloads.
- Training managers on the implications of this Employee Law Change will minimize disruptions.
Expansion of Paid Family and Medical Leave
A federal initiative to expand paid family and medical leave requires employers with more than 50 employees to provide up to 12 weeks of paid leave annually. This Employee Law Change prioritizes work-life balance and employee well-being.
Impact on HR:
- Updating leave policies and educating employees on their rights.
- Implementing systems to track and manage leave requests effectively.
- Anticipating potential staffing shortages and planning accordingly.
For practical tips on effectively managing employee benefits, check out our guide: Employee Benefits Management in Small Enterprises.
Enhanced Anti-Discrimination Laws
Changes to Title VII of the Civil Rights Act will broaden protections for employees based on gender identity and sexual orientation. These Employee Law Changes foster greater inclusivity in the workplace. Impact on HR:
- Revising anti-discrimination policies and ensuring compliance with the updated laws.
- Conducting training programs to foster a more inclusive workplace culture.
- Establishing clear reporting channels for discrimination complaints.
Stronger Data Privacy Regulations
With the passage of the Federal Employee Data Privacy Act, stricter requirements for collecting, storing, and using employee data will be enforced. This Employee Law Change ensures that personal information is safeguarded. Impact on HR:
- Auditing current data storage practices to ensure compliance.
- Providing training on data handling and security protocols.
- Updating privacy policies and communicating them clearly to employees.
Challenges for HR Professionals
While these Employee Law Changes bring significant benefits for employees, HR professionals may face several challenges:
- Increased Administrative Burden: Compliance with new regulations often requires revising systems, updating policies, and ensuring thorough documentation.
- Cost Implications: Higher wages, overtime pay, and expanded benefits could strain budgets, especially for small businesses.
- Communication Gaps: Ensuring all employees understand their rights and changes to company policies requires effective communication strategies.
How to Prepare Your Business for 2025
Conduct a Compliance Audit
Regularly review your HR policies and practices to identify areas needing adjustment to meet the new Employee Law Changes.
Train Your Team
Educate managers and HR staff about the upcoming Employee Law Changes to ensure they are well-equipped to implement new policies.
Review Employee Contracts
Update contracts to reflect changes in wages, overtime eligibility, and leave entitlements.
Engage Legal Experts
Consult with employment law specialists to navigate complex legal updates and mitigate risks.
Conclusion
The legal landscape for HR is evolving rapidly, and 2025 is set to bring some of the most impactful Employee Law Changes in years. By proactively addressing these updates, businesses can stay compliant, support their employees effectively, and maintain a competitive edge. Leveraging tools like Humadroid can further simplify compliance and empower HR teams to focus on strategic goals.

